Definitions
The symbol colon-equals ':=' means "Is Defined As". Links are just to the definitions on this page, not to other pages.
Environment := A geometrically structured region in which interactions occur.
May include self.
Domain := A region, such as an area or volume, of accommodation or containment.
Influence := A change in state propagated through the environment. .
Greater Influence means more modification. Verb: to induce change; noun: the amount of induced change.
Perception := Detection of environmental influence across a boundary.
E.g. physical senses; instruments; superposition of waveforms.
Interaction := Mutual influence between structures through shared environmental coupling.
Interaction Constraints: Proximity in Space and Time, which determines waveform coherence.
Quantity := Integral magnitude of scaling.
E.g. the number of particles; amount of mass or energy; or how many waveforms are in superposition.
RateOfDirection := Rate of Direction.
E.g. velocity as a change in distance over time, with rate as the magnitude of Speed in a Direction, which characterizes a vector; also a change in area or volume over time.
FocalRegion := Domain of Interaction Probability.
E.g a volume or area. May compress toward a point in an instant, or diverge in a sphere of eternal persistence - as we detect light from billions of years ago and billions of light years away.
Communication := Receipt of Transmitted Information.
For communication to occur, the intended information transmitted must be received - not some corrupted information due to transmission mechanisms or misunderstanding of the information content.
Information := Anything that can be represented by a Waveform.
Light has a waveform, so information can include anything seen, felt as heat, or encoded in radio waves, and so on. Audio has a waveform too, so information can include anything spoken or heard. In quantum mechanics, anything can be represented by its Schrodinger Wave Equation in principle, so information can come from all matter and energy. Digital bits are encoded as voltage levels as amplitudes of electrical oscillations which have waveforms that can be displayed on an oscilloscope. I know of no counter-examples of information that cannot be expressed in a waveform, since all words and symbols can be spoken, and all depictions can be shown. What we directly experience as an awareness is communicated via information in words or pictures, which are contained in waveforms. Whether such a direct experience is contained in a waveform is a matter of philosophical debate at this point, since we have not identified the core object that characterizes influence. For example, we can trace the roots of the mechanism of taste, but not what contains the preference for some flavors over others; we know the path of vision into the brain and visual cortex, but not the host of the preference of some colors over others.
Transmission := Motivated Influence to convey Information.
Communication is deliberate. There is a physical mechanism to sustain the transmission, and this generalizes to some environmental influence. The information can be contained in a waveform, so the influence generates waveforms like light, radio waves, or sound.
Reception := Recognition of Transmitted Information.
Transmitted information is a waveform in the environment. Detection of that waveform is required, along with correct interpretation of the waveform to deconstruct the encoded information that was deliberately transmitted.
Word := Unit of Information.
Words carry information, encoded as waveforms to be heard or read.
Photon := Unit of Light.
In physics, the photon is called the carrier of information as a wave-particle duality.
Light := Carrier of Information (m, dx, dt, C, D) via Electromagnetic QED Interactions.
Light is Energy, and energy has frequency-ranges that characterize its properties, such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet light, x-rays, and cosmic rays.
Sound := Carrier of Information via Audible Waveform Interactions.
Note (context: musical) := Unit of sound (loudness, timing, duration, tone, pitch).
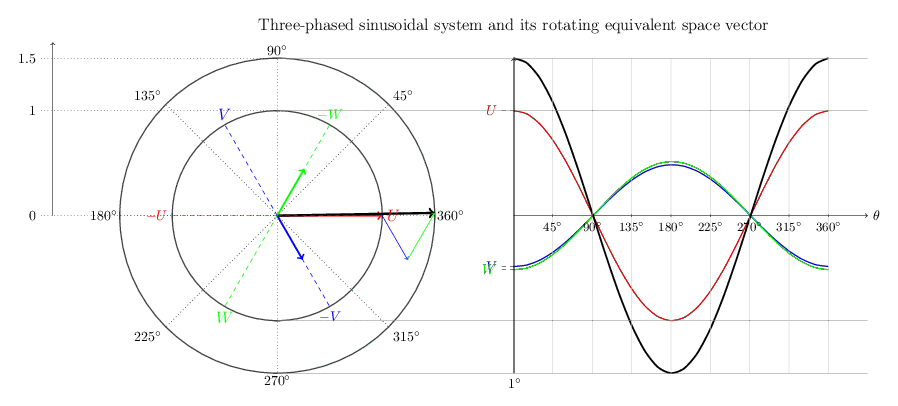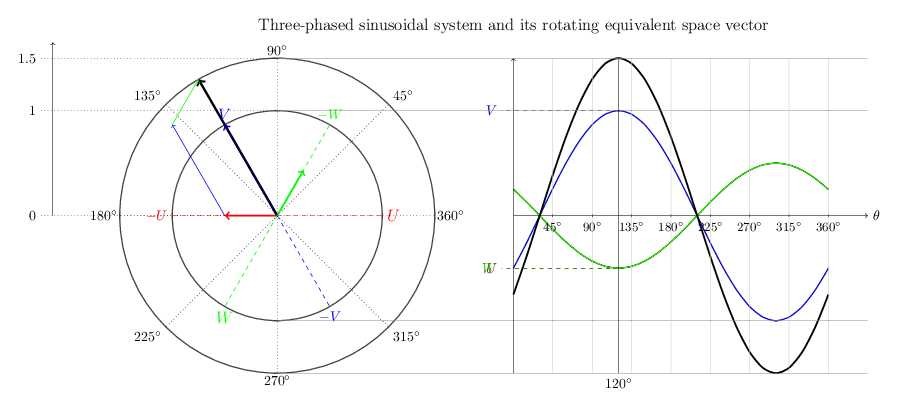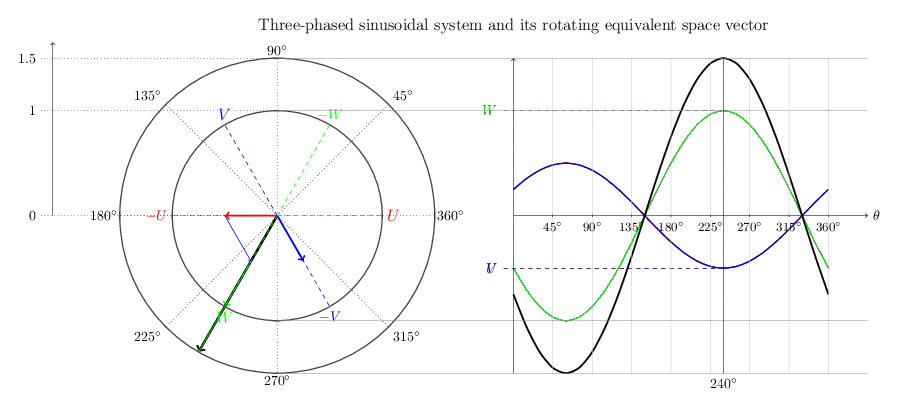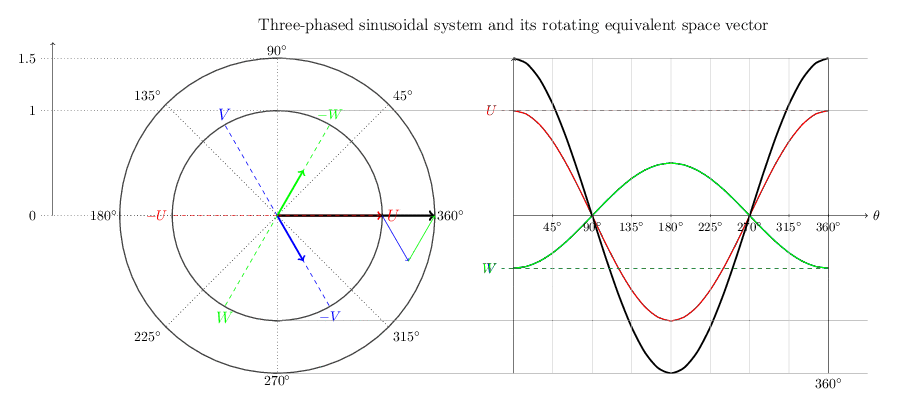
Waveform := 2D Oscillation of a repeating pattern of harmonics as fundamental plus overtones.
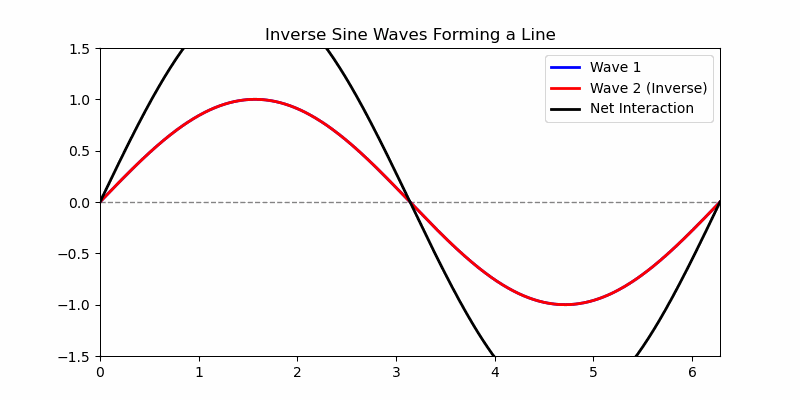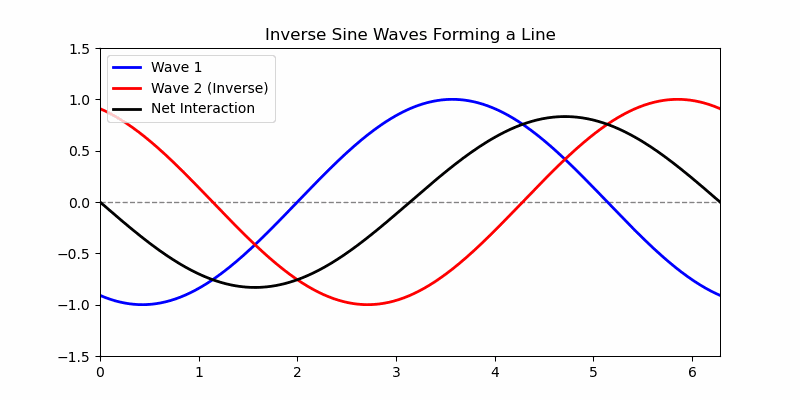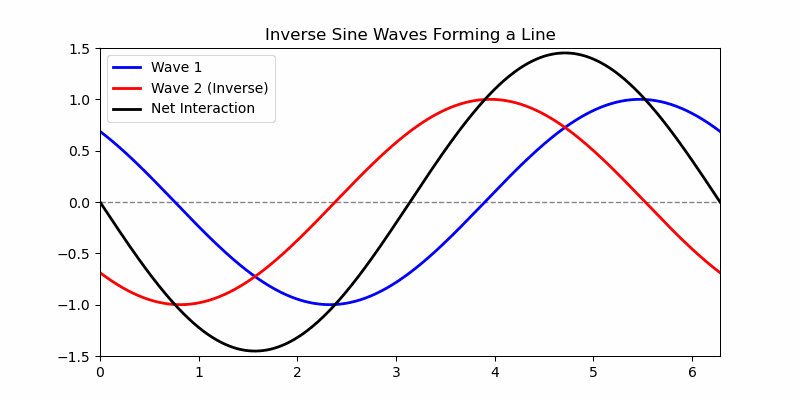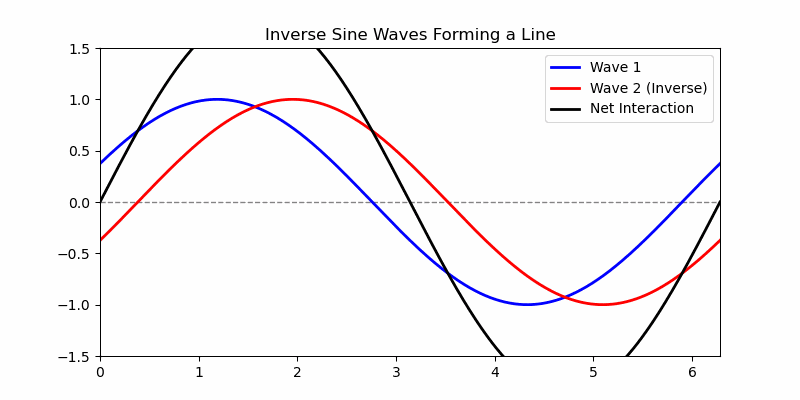
The simplest waveform is a straight line. A typical simple (non-degenerate) waveform is a kind of sine wave, which looks like a symmetrical oscillation in height (amplitude) above and below a central axis with corresponding peaks and troughs as local maxima and minima of the amplitude of the wave. Note that two opposite waveforms, where the peaks of one align directly over the troughs of the other, in combination yield a flat line, as all the oscillations are exactly counter-balanced by the complimentary wave and there is no net non-zero peak or valley in the combination. Noise cancelling earphones work by recognizing the incoming audio net waveform and generating a complementary inverse waveform that gets added to the incoming signal in real time, resulting in a net "no wave" quiet contribution of the external environment.
Superposition (verb) := The process by which interacting waveforms combine, producing a composite rotationally oscillatory geometry.
Superposition (noun) := A stable composite formed by sustained interference alignment, creating an internal Environment in which constituent waveforms continue interacting while expressing a net interaction externally.
Superposition is the dynamic balance of interacting tendencies, not the cancellation of amplitudes.
Musical overtones are the harmonics of the sound wave, and are the reason notes having the same pitch, e.g. A, B, C…, sound different among different instruments - their overtones are different, even though the fundamental frequency of vibration is the same. The sound of the orchestra is the harmony of all the instruments' waveforms with their characteristic overtones in superposition as the air induces a corresponding superposition pattern on our ear drums. Notice that all individual waveforms in a live performance maintain their independent existence, even as the final superposition conveys all the harmonized information, even phantom tones not physically played on any instrument. In light we know that constituent colors can be separated by a prism or a crystal, but the original light's resultant color is the blend of those contributing colors. So we see that the individual waveforms persist, even while a net combination interacts in the environment. Think of a sandy beach, with rolling dunes that undulate, and wind-blown ripples along the surface of the beach and dunes. Average irregular grains of sand, like little subatomic particles (in a wave-particle duality), accumulate into curves - and that is a tangible example of superposition, where the Dune is a stable or 'coherent' superposition, though it varies with weather, wind, and rain, perhaps tide and other environmental interactions - but persists over time, gaining new sand with some washed or blown away, and is less variable than the ripples that form upon and around it.
This animation shows a blue wave flowing from left-to-right and a red wave flowing right-to-left. The black wave oscillation is up and down, not side-to-side, and is the superposition of the two waves. There are two kinds of superposition, what are called 'constructive interference' and 'destructive interference'. Constructive interference is where adding the waves together forms a higher peak, like adding to positive numbers makes a larger positive number - and we can see where the black superposition curve grows from the combination to be higher than the red or blue wave, even off the top, and similarly the troughs reinforce like adding two negative numbers into an even lower negative number. Destructive interference is where adding the waves together forms a lower peak, as the black curve oscillates from off-the-animation high to off-the-animation low and everywhere in between, including a flat line at the moment of exact cancellation of the red and blue waveforms. That flat line occurs in the superposition where the values of the waveforms are equal and opposite, and cancel. In math symbols, it's where v=dx/dt→0/0=c, and an electron like the blue wave and positron like the red wave interact as matter and antimatter, and at the moment of exact cancellation the velocity equation becomes the limit as 0/0, and the calculus shows that in the limit of speed as dx or dt goes to 0, c=dx/dt, so the interaction obtains v=c as a photon, with all the photon properties equal to 0 as a result of the destructive interference in superposition, and the matter and antimatter become a photon of Light.
.
Frequency := Number of repeating waveform patterns per unit distance.
Wavelength := Distance between corresponding elements of a repeating harmonic pattern.
Coherent := context: Waveforms as 'Geometric alignment of harmonic overtones.' context:Semantics as 'Logically Valid'.
Awareness := Directly experienced perception.
Conscious := Experiencing Preferred Awareness.
Free Will := Determination of relative preference importance.
Choice := emergent property of distinction plus association.
Distinction := A boundary that partitions interactions into elements that are “included” and “excluded”.
Association := A relationship between two distinguished entities based on shared attributes or co‑occurrence.
Connection := A relationship formed from the intrinsic structure or mechanism of the entities involved.
Correlation := A statistical relationship where changes in one intrinsic property predict changes in another.
Causation := A relationship where one event or state invariantly produces another.
Satisfaction := Magnitude of achievement of a Preferred-State.
e.g. a spectrum from 0 as totally not satisfied to 100 as completely satisfied;
e.g. a spectrum from -50 as totally not-preferred to 50 as totally preferred.
Preference := Qualified Experience of Perception.
Preferences are relative among conscious awarenesses, yielding an associated Importance as the relative Priority.
Types of Preference: Objective and Subjective.
Importance := Relative magnitude of preference satisfaction motivation.
Priority := Relative Importance of a Preference to overall Satisfaction.
Motivation := Priority to increase Satisfaction.
Spirit := Motivated Preference that interacts with its soul.
Soul := Substrate that Sustains its Spirit
MotivatedEntity (ME) := Perceptive structure that Prioritizes Preferences.
Objective := Having to do with unbiased logical validity.
Subjective := Having to do with sensory perception.
True := Objectively Correct from all Perspectives.
False := Not True.
Truth := True without bias or deception.
Perspective := Observer-Dependent Observation.
Observation := Perception of Environmental Influence
Physical := Interaction via Geometry-Energy-Mass-Space-Time relationships.
Spiritual := Interaction via Motivated Choice.
Life := Generative Replication of Perceptual Structure.
Reality := The Combined Physical and Spiritual.
Seed := Persistent coherence capable of replication under proper conditions.
Existence := Having Influence.
Duality := Distinct cooperative aspects of one composite interaction.
In physics, Light is characterizes as a wave-particle duality. It exhibits both aspects under different conditions, but it is one unified nature of light, the whole as the duality which interacts in its environment. Neither one aspect nor the other, but both simultaneously.
A duality is formally written like this: Aspect1<>Aspect2.
Triality := A duality with a Characteristic Interaction in its environment.
The interaction of a duality has a characteristic presentation to its environment; the duality of aspects have a characteristic net interaction in their environment. A triality is formally written like this: Aspect1<Characteristic Interaction>Aspect2. Examples:
-
The wave-particle duality of Light: Wave<Color>Particle, where the Color (and other properties) are characteristic of the waveform Frequency and Amplitude and points of synchronization where particle interactions can occur.
-
A musical instrument string vibrates with a characteristic sound as pitch, timbre, and loudness: Vibration<Sound>String.
-
Specific software running on a device produces a characteristic App: Software<App>Device
-
A Motivated Entity (ME): Spirit<ME>Soul
-
A personality of the mind revealed by the body: Mind<Personality>Body
Emotion := Internal coherence signals representing changes in preference satisfaction.
Reasoning := the assembly of self‑evident truths into clear structures through concise logic.
Identity := The persistent invariant structure maintained across recursive generative cycles.
Identity is what remains stable as the system changes.
Attention := Directed allocation of perceptual and generative resources toward prioritized preferences.
It’s the focusing of generative capacity — the mechanism that selects which reduced projection becomes behaviorally relevant.
Attention is the interface between perception and action.
Curiosity := Motivation to reduce uncertainty by increasing coherence between perception and internal structure.
It is the drive to improve the alignment between internal models and external reality.
Curiosity is the generative impulse toward deeper alignment.
It is the engine of learning.
Agency := Self‑determined generative action guided by prioritized preferences.
Agency is the operational expression of Free Will. It is the self‑directed expression of generativity.
It is the perceptual structure acting as a cause rather than merely an effect.
Spirituality := Awareness of and alignment with coherence beyond one’s perceptual boundary.
Spirituality is the felt recognition of being embedded in a coherence larger than one’s own boundary.
Ethics := Behavioral constraints that preserve and enhance generative coherence.
Aesthetics := The felt recognition of coherence in perceived structure.
Beauty is coherence made perceptible.
Evolution := Recursive generative variation constrained by stability of invariants.
Evolution is the geometry of generativity under constraint.
Society := A network of interacting structures coordinating generative stability.
Society is the recursion of intelligence across boundaries.
Conclusions
Quantity is the number of discrete elements, so anything that arises from Superposition of integral components is Quantized by definition.
I directly experience perceptions, therefore Awareness exists.
I prefer some perceptions to others, therefore I am conscious and Consciousness exists.
Since consciousness exists, preferred perceptions exist. Selecting among them embodies "Free Will"; not violating causality, sorting experiences and priorities which culminates in a decision to interact some way, or not.